

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-15 Origin: Site











Choosing the right pipe helps work run better in 2025. RTP and TCP pipes are not the same. They have different builds, uses, and fit for jobs. RTP uses strong plastic. This makes it bend easily and stops rust. TCP uses fibers that run all the way through. This makes it strong under high pressure. New reports say RTP is growing the fastest. TCP works best in tough places.
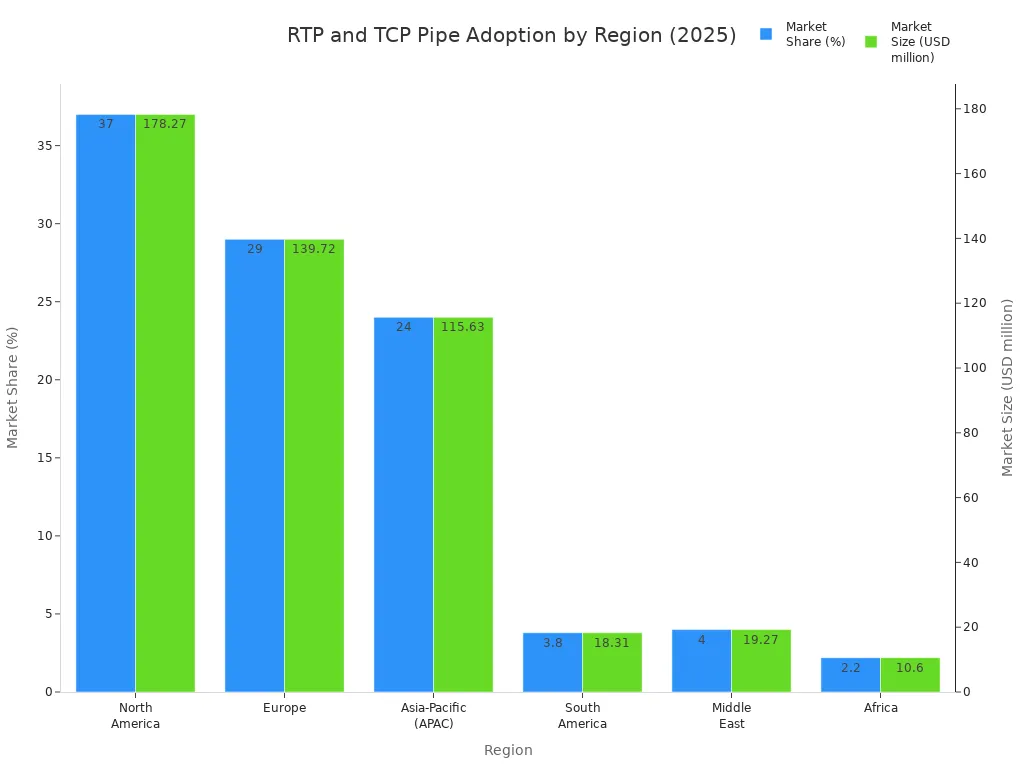
Segment/Region | Market Share (2025) | Market Size (USD million, 2025) |
|---|---|---|
North America | 37% | 178.27 |
Europe | 29% | 139.72 |
Asia-Pacific (APAC) | 24% | 115.63 |
South America | 3.8% | 18.31 |
Middle East | 4% | 19.27 |
Africa | 2.2% | 10.60 |
Unitedpipe is a leader in RTP pipes. They use new tech and check quality closely. Every job has its own problems. Companies should pick the pipe that fits their needs best.
RTP pipes have layers of metal and plastic. This makes them bend easily. They are strong and simple to put in. People use them on land or in shallow water.
TCP pipes are made from fibers and plastic pressed together. This makes them very strong and light. They work well in deep water and where pressure is high.
Both RTP and TCP pipes do not rust. They also do not get damaged by chemicals. RTP bends more easily. TCP stays stiff and strong for hard jobs.
You pick the right pipe based on the job. RTP is good for jobs that need bending and save money. TCP is better for tough, high-pressure jobs in the ocean.
Unitedpipe is a leader in RTP pipes. They use new technology and check quality. This helps companies get safe and strong pipes for many uses.

It is good to know how RTP and TCP pipes are different. RTP means reinforced thermoplastic pipe. TCP means thermoplastic composite pipe. People mix up these names sometimes. Both use special plastics and fibers. But they are built in different ways and used for different jobs.
RTP has many layers. It has a plastic liner, a strong layer, and a tough outside. This makes it strong like metal pipes but also bendy like plastic. RTP works in places with medium or high pressure. You see it in oil, gas, and factories.
TCP is made with only plastic and fibers. It does not have any metal. Makers wrap the materials around the pipe. This makes TCP light and easy to move. TCP does not rust or get old fast. It works well in deep water and rough places.
RTP is a mix that handles pressure and lasts long. It is good for land and shallow water jobs.
TCP is very light and does not rust. It uses heat to join pieces fast. You find TCP in deep water oil and gas fields.
RTP and TCP help with green energy now. They move hydrogen and help with carbon capture. They are good for new jobs because they handle pressure and do not rust.
Feature | RTP (Reinforced Thermoplastic Pipe) | TCP (Thermoplastic Composite Pipe) |
|---|---|---|
Structure | Many layers, metal and plastic | All plastic, fibers |
Pressure Handling | Medium or high | High, deep water |
Corrosion Resistance | High | Very high, no metal |
Weight | Not too heavy | Very light |
Installation | Quick, bends easily | Quick, uses heat to join |
Typical Application | Oil, gas, factories, green energy | Deep water, tough places, green energy |
Note: RTP and TCP pipes help with new piping needs. They work for different jobs because of how they handle pressure, rust, and how they are put in. Each one is best for certain jobs in piping.
RTP pipes have many layers. Each layer does something special. The liner layer is made from thermoplastics like PE100, PE-RT, PEX, PA, or PVDF. This layer keeps chemicals out and stops gas from leaking. The reinforcement layer uses steel cord, aramid fiber, glass fiber, or polyester. These wrap around the pipe at about a 55-degree angle. This makes the pipe strong and lets it bend. The outer layer uses HDPE, PA, or PVDF. It protects the pipe from sun, water, and weather.
Layer Type | Materials Used | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
Liner Layer | PE100, PE-RT, PEX, PA, PVDF | Chemical resistance, gas tight, smooth flow |
Reinforcement | Steel cord, aramid, glass, polyester | High strength, flexibility, pressure resistance |
Outer Layer | HDPE, PA, PVDF | UV protection, durability, environmental shield |
Unitedpipe is a top company for RTP pipes. They spend money on research and making new products. Their factories use new machines and check quality often. Every pipe is made to be safe and work well.
RTP pipes are flexible and do not rust. They bend easily, so putting them in is quick. They do not get rusty or damaged by chemicals, so they last longer than metal pipes. The layers can move a little, which helps the pipe handle stress. RTP pipes can be rolled up, so moving and installing them is easy. They can handle pressure up to 32 MPa, so they work for many jobs. Unitedpipe sells gas tight RTP and flexible composite pipes for different uses.
Flexible and simple to put in
Strong against rust and chemicals
Light, so easy to move
Can be rolled up for fast setup
Can handle up to 32 MPa pressure
RTP pipes are used in many fields. Oil and gas companies use them for flowlines, gathering lines, and water injection. They work on land and in the sea. Oil and gas companies like them because they are quick to install and need little fixing. Mining companies use RTP pipes to move slurry and tailings. Water and sewage systems use them because they last long and do not leak. Chemical plants use RTP pipes to move fluids safely. Unitedpipe gives these industries strong and trusted pipes.
RTP pipes help companies have less downtime and be safer. They are a new choice instead of steel for important pipes.
TCP pipes are made in a special way. Makers use a melt-fusing process. This puts glass or carbon fibers inside a plastic mix. Each layer sticks together very well. The idea comes from how planes are built. This makes the pipe strong and light. TCP pipes can be much lighter than metal pipes. Some are up to 80% lighter. They use materials like carbon fiber and plastics such as PVDF, PE, PA12, or PEEK. The plastic mix lets the pipe bend and stretch. Makers sometimes add heavy coatings. These coatings help the pipe stay in place on the sea floor. The process follows strict rules like DNVGL-ST-F119. This makes TCP a trusted pipe for use in the ocean.
Component | Material Options | Function |
|---|---|---|
Reinforcement | Glass or carbon fibers | Provides strength and stiffness |
Polymer Matrix | PVDF, PE, PA12, PEEK | Binds fibers, adds flexibility |
Weight Coating | Heavy polymer compounds | Ensures seabed stability |
TCP pipes are strong but not heavy. The fibers inside make them tough and easy to move. Because they are light, they cost less to put in. Projects can finish faster. TCP pipes do not rust or get hurt by chemicals. They last a long time in hard places. The way they are made helps them handle high pressure. They can also take on moving loads. TCP pipes bend well, so they fit in tricky spots. They do not rust, even in salty water or near chemicals. They are tough and do not break easily. This makes them good for hard jobs.
Strong but light
Easy to move and quick to set up
Do not rust or get hurt by chemicals
Bend to fit tricky places
Work well for a long time in tough spots
Tip: TCP pipes can take more pressure than most other plastic pipes. This is why they are picked for deep water and ocean jobs.
In 2025, TCP pipes are used in deep water and ocean oil and gas work. Companies use them for jumpers, flowlines, and risers under the sea. They work well in deep places like Brazil’s Campos Basin, which is 1,500 meters deep. TCP pipes do not get weak from CO₂, so they are good for many wells. Because they are light and do not rust, they are easy to put in with normal ships. This saves money and time. TCP pipes also help with new ways to connect pipes under the sea. This lowers leaks and makes things safer. Besides oil and gas, TCP pipes are used for water, chemicals, mining, and building projects. Their strength and ability to bend make them a top pick for new pipelines.
RTP and TCP pipes both handle pressure well. RTP has many layers. One layer makes it strong under pressure. TCP is made with fibers inside the pipe wall. This gives TCP more strength and makes it stiff. Studies show both pipes work in hard places. RTP is good for oil, gas, and water jobs. TCP is best for deep water and high-pressure work. It does not get weak from hydrogen. This makes it good for moving hydrogen. Lab tests show TCP can take pressure, pulling, and heat. RTP also does well in labs. But TCP is usually stronger because of how it is built.
Pipe Type | Pressure Resistance | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
RTP | High | Oil, gas, water, mining |
TCP | Very High | Deepwater, subsea, hydrogen |
Note: TCP pipes are often picked for high-pressure jobs. They are chosen when strength and safety are most important.
RTP pipes bend a lot. They fit into tight or odd spaces. This helps when the job needs quick changes or is in rough land. TCP pipes are stiffer. The fibers make them strong but less bendy. TCP is best for straight or fixed lines. RTP can be rolled up and moved fast. TCP needs careful work to put in because it is stiff.
RTP: Bends easily, simple to move, good for curvy paths.
TCP: Stiff, keeps its shape, best for straight lines.
Cost is important when picking pipes. RTP pipes cost less to make. Their layers and soft materials keep prices low. They are good for jobs that need to save money. TCP pipes cost more at first. The strong fibers and special build make them pricey. But TCP lasts longer in hard places. It needs less fixing over time.
Pipe Type | Initial Cost | Long-Term Value |
|---|---|---|
RTP | Lower | Good for most industries |
TCP | Higher | Best for harsh settings |
Tip: Companies should think about both the first price and future savings when picking RTP or TCP.
RTP pipes are easy to put in. They bend, so workers can use long pieces. This means fewer joints and faster work. It also saves on labor costs. TCP pipes are light but stiff. They need special tools and care to install. TCP is great for deep water or tough jobs. Both types are faster to install than steel pipes.
RTP: Fast to set up, fewer joints, easy to move.
TCP: Needs careful setup, best for deep water or fixed places.
RTP and TCP pipes both fight rust and chemical harm. RTP has layers that are not stuck together. This makes it bendy and cheap, good for land or shallow water. TCP has layers melted together. This makes a strong wall. TCP is tough against pressure inside and out. It also handles pulling better. TCP is good for deep water and hard places. Both last longer than steel and work with strong fluids.
Feature | RTP | TCP |
|---|---|---|
Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
UV/Weather Protection | High | High |
Suitability | Onshore, shallow water | Deepwater, harsh environments |
Callout: TCP pipes give extra safety in the hardest jobs. RTP is a smart and cheap choice for easier places.
Picking a pipe for high pressure needs careful thought. Both RTP and TCP work well, but they are made and tested in different ways.
TCP is made with machines that melt and join the parts. If not watched closely, this can cause problems.
Checking composite pipes is hard because tools may be too big or the pipe bends too much.
Some ways to check pipes do not always give exact answers.
The rules for testing are not the same. API RP15S uses a long test with pressure. DNV GL-RP-F119 wants more checks and details.
Pipes need to be tested for a long time. Short tests might not show if the pipe is really strong.
Knowing what the pipe is made of and how it is made helps keep things safe.
Tip: Always look at the testing rules and how long the tests last before picking a pipe for high pressure.
Flexibility is important for many jobs, especially when pipes must bend or go over bumpy ground. New studies say RTP is one of the best for bending. It has many layers that stop rust and breaking. It is light, so it is easy to put in on land or in water. Companies pick RTP when they need a pipe that bends but does not snap. TCP can also bend, but RTP is better for jobs with lots of bends or movement.
Cost matters a lot when picking pipes. The table below shows how RTP and TCP compare for big projects:
Aspect | TCP Pipes | RTP Pipes |
|---|---|---|
Structure | Fully composite, continuous fiber | Multi-layer, reinforced thermoplastic |
Strength & Rigidity | Higher, for high-pressure and subsea | Flexible, lightweight, up to 70 bar |
Installation & Transportation | Lower costs offshore, simplified setup | Easy installation, dominates onshore |
Durability & Maintenance | Long service life, low maintenance | Durable, corrosion resistant, low maintenance |
Cost Considerations | Higher upfront costs | Cost-effective over time |
Market Growth | Rapid, especially offshore | Strong, especially onshore |
Note: Both types of pipes save money over time because they last long and do not need much fixing.
Pipes in tough or rusty places must be strong and last a long time. Real-world data shows non-metal pipes like RTP do well in these spots.
RTP is strong, bends well, and does not rust.
It works for gas pipes on land and in the sea, even where it is rusty.
Pipes with plastic linings like HDPE or PVDF also fight off chemicals and heat.
Companies use RTP because it is tough and has worked well in the field.
Callout: For tough places, RTP is a safe and trusted pick.
RTP and TCP pipes are used for different jobs in many industries. RTP has many layers that are not stuck together. It is good for jobs on land and places that are not too tough. TCP is made with all its parts joined tightly. It uses strong materials and works well in deep water and places with a lot of pressure.
RTP is best for land jobs, lower pressure, and normal heat.
TCP is good for sea jobs, deep water, and hard places.
TCP is lighter and easier to put in faraway spots.
Pipe Type | Best Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
RTP | Onshore, moderate | Flexibility |
TCP | Offshore, deepwater | High strength |
Picking the right pipe keeps people safe and helps work go well. Unitedpipe can help companies pick the best RTP pipe. Their skills and new tools help make sure projects work out right.
RTP pipes have many layers. They use thermoplastic liners and strong support. TCP pipes have fibers inside a plastic mix. RTP pipes bend easily and are strong. TCP pipes are light and handle high pressure well.
Companies use RTP pipes in oil, gas, and mining jobs. They also use them for city water projects. RTP pipes work for flowlines and moving water or slurry. Many pick RTP because it is quick to set up and does not rust.
RTP and TCP pipes last a long time. How long depends on where and how they are used. Most RTP pipes work for more than 20 years. TCP pipes can last even longer in tough places.
Yes, both types of pipes fight off chemicals. RTP pipes use liners like PE100 or PVDF. TCP pipes use strong plastics and fibers. They protect against acids and other harsh liquids.