

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-26 Origin: Site











Reinforced thermoplastic pipe is changing oil and gas pipelines with its smart design and strong performance. Reports from the industry say these pipes have many benefits:
It does not rust from salt, hydrogen sulfide, or carbon monoxide, so it lasts longer.
It is strong but light, so it is easier to put in than steel.
It bends easily, so it can be used in tough places and is safer.
It can handle high pressure and heat because it does not let much through and is very strong.
Reinforced thermoplastic pipes help the environment by needing less fixing, having fewer leaks, and costing less. RTP is being used more as companies want safer, quicker, and better ways to build pipelines.
does not rust or get damaged by chemicals. This helps pipelines last longer and stay safe. RTP is strong but also light. This makes it easier and quicker to put in than steel pipes. Its flexible design lets pipelines deal with hard things like earthquakes and moving ground. RTP saves money because it needs fewer repairs. It also gets installed faster and costs less to move. Using RTP helps the environment. It lowers leaks, pollution, and energy use when working on pipelines.
Reinforced thermoplastic pipe has many layers. This helps it work well in oil and gas pipelines. It has a thermoplastic liner, fiber reinforcement, and an outside cover. The liner is usually made from HDPE. It stops leaks and keeps out chemicals. The fiber layer uses aramid, carbon, or glass fibers. These fibers are wrapped around the pipe in a spiral. This layer holds pressure and weight inside the pipe. The outside cover is made from the same plastic as the liner. It protects the pipe from things that could hurt it.
Hybrid construction mixes these materials to make the pipe stronger. In bonded pipes, the fiber tape sticks to the liner and cover. This makes the pipe wall solid. It stops the liner from falling in or the cover from coming off when pressure changes. Non-bonded pipes let the layers move on their own. This makes the pipe bend easier and helps make it faster. Non-bonded polyester fiber reinforced HDPE pipes are used a lot in oil fields on land. They cost less and are easy to make.
Note: The hybrid structure helps the fibers stick to the plastic better. Surface treatments like fluorination make the bond stronger. This helps the pipe handle more weight and work better. Wrapping the tape in a spiral lets companies make long pipes. This keeps the pipe strong and bendy at the same time.
Fiber reinforcement is very important for making the pipe strong and flexible. Companies pick different fibers for different jobs:
Synthetic fibers like aramid and glass do not rust and are pretty strong.
Carbon fibers are the strongest and last a long time, even when it is hot.
Steel wire is used when the pipe needs to hold very high pressure.
Fiber Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|
Carbon Fiber | PAN-based, high modulus, high strength | Maximum strength, resists moisture and acids |
Glass Fiber | E-CR and S-glass, corrosion resistant | Moderate strength, lightweight, cost-effective |
Aramid Fiber | Aromatic polyamide, impact resistant | High tensile strength, fatigue resistance |
The many layers protect the pipe from rust better than steel pipes. The inside liner keeps out chemicals like CO₂, H₂S, and salty water. The fiber layer makes the pipe strong and keeps it from wearing out. The outside jacket keeps things from hurting the pipe. This design helps the pipe last a long time and work well in tough places.

Steel pipes can rust when they touch certain liquids. This rust can cause leaks and breaks. Leaks can hurt nature and cost a lot to fix. Fiberglass pipes last longer because they do not rust easily. They use a special resin that keeps water out. This stops rust from forming. Reinforced thermoplastic pipe is even better at stopping rust. It does not break down in tough places or with strong liquids. Companies do not need to pay for special coatings or many repairs. The thermoplastic and fiber layers make the pipe last a long time. RTP saves money by cutting costs by about 35%. It also means less need for extra protection or new pipes. This makes RTP a smart choice for oil and gas pipelines.
Strength-to-weight ratio shows how strong a pipe is for its weight. Steel pipes are heavy but strong. Fiberglass and RTP have better strength for their weight. RTP uses fibers like glass or aramid. This makes it strong and light at the same time. This helps crews move and put in the pipes more easily. The table below shows how different pipes compare:
Material Type | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Strength-to-Weight Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
Steel | 7.85 | 483–690 | High density, moderate strength |
GFRP | 1.25–2.10 | 483–1600 | Higher ratio, lighter, strong |
CFRP | 1.50–1.60 | 600–3690 | Much higher ratio, very strong |
AFRP | 1.25–1.40 | 1720–2540 | Very high ratio, strong, light |
BFRP | 1.90–2.10 | 600–1500 | Higher ratio, strong, light |
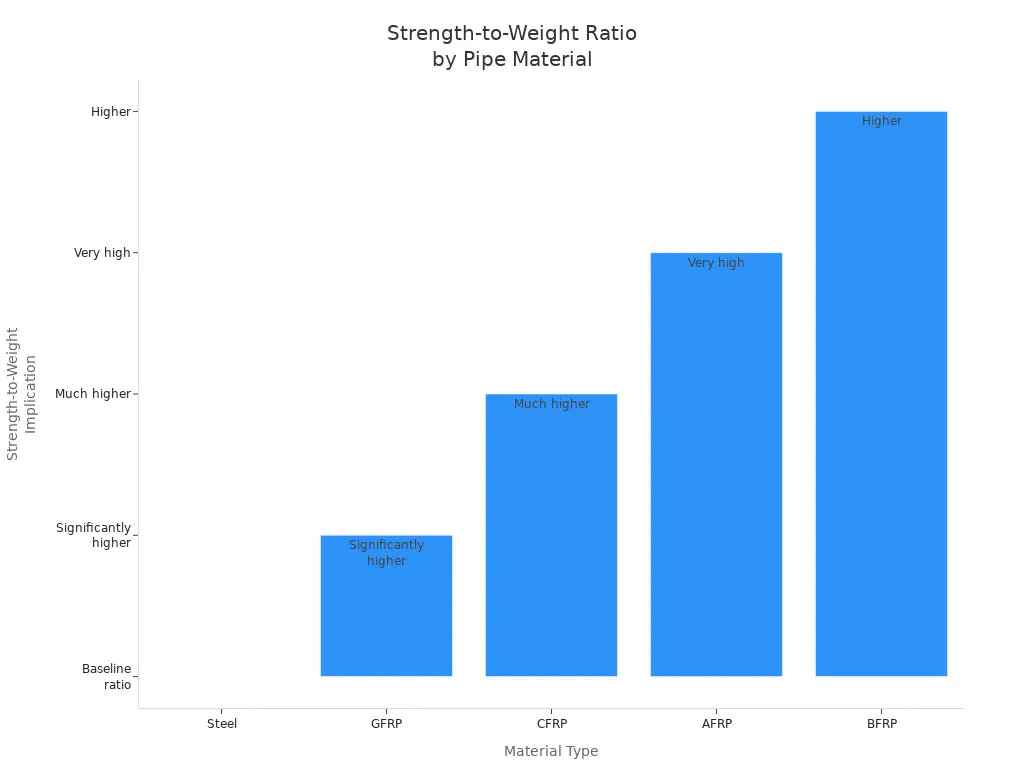
RTP is light, so crews can carry and install it faster. This also means it costs less to move. Its high strength-to-weight ratio helps it work well in hard jobs.
RTP bends more than steel or fiberglass pipes. It can move with the ground if there is an earthquake or if the ground shifts. This is important in places where the ground is not steady. RTP does not need extra supports when being put in. This makes it good for far away or rough places. Long coils and quick setup help crews finish jobs faster and cheaper.
Reports show that spoolable RTP can be put in 40% to 80% faster than steel pipes. Fewer workers and less gear are needed because RTP does not need welding. It also means crews do not need to clear as much land. This helps nature. Offshore jobs save more money with RTP because steel is costly to install in the ocean.
RTP does not rust, so fixing it costs less.
It is light and comes in coils, so putting it in is cheaper.
It works well for pipes up to 30 miles long, and even up to 50 miles when thinking about running costs.
Offshore jobs save more because steel is expensive to install there.
RTP bends, so it can handle earthquakes and other problems, making it good for far places.
Projects finish faster with RTP. For example, Saudi Aramco finished three weeks sooner than with other pipes. New RTP technology helps crews work even faster and spend less money.
Tip: Companies that want fast, easy, and strong pipelines often pick RTP. It is quick to put in, easy to take care of, and works well in tough places.
Reinforced thermoplastic pipe works well in tough oil and gas jobs. It can handle very high pressure and big changes in temperature. The table below shows how much pressure and heat RTP can take:
Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
Pressure Rating | 2 MPa to 32 MPa |
Temperature Range | -40°C to 110°C |
These numbers mean RTP can move oil, gas, and water safely. It works even in cold places or deep underground. Unitedpipe makes RTP that meets these rules or does even better. This keeps pipelines safe and working well. Workers use RTP for many jobs, even when steel or fiberglass pipes might break from rust or heat.
RTP lasts a long time, so it does not need to be replaced often. Steel pipes can rust and need special coatings. RTP does not get damaged by chemicals or wear out easily. Fiberglass reinforced plastic pipes also fight rust well. These pipes can last from 10 to 40 years, depending on where they are used and how they are cared for. In places with lots of chemicals, RTP and FRP last longer than steel, which needs more fixing because of rust and leaks.
RTP does not rust from chemicals like hydrogen sulfide or saltwater.
It stays strong and bendy for many years.
Good setup and care help it last even longer.
Unitedpipe uses strong materials and checks quality carefully. This makes sure the pipes work well, even far away or in hard places. Workers have fewer problems and spend less money fixing things, so the job runs better.
RTP helps protect nature in oil and gas work. It makes less pollution than steel pipes when being made, moved, and put in. The table below shows how RTP helps the environment:
Aspect | Evidence Supporting Carbon Footprint Reduction by RTPs |
|---|---|
CO2 Emissions Reduction | Up to 60% less CO2 than steel pipes from start to finish |
Energy Footprint Reduction | Up to 50% less energy used than steel pipes |
Material Characteristics | Lighter weight means less pollution when making and using |
Corrosion Resistance | RTP does not rust, so less fixing and less pollution |
Installation Efficiency | Easier and faster to put in, so less pollution and cost |
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) | Less energy and pollution over the pipe’s life, even when recycled |
Industry Adoption | Over 5000 km of RTP used by Saudi Aramco, showing it works well and saves money and nature |
Rules in North America and other places want safer and greener pipelines. RTP can be recycled and does not get hurt by chemicals. This helps companies follow these rules. Unitedpipe’s RTP fits these needs and gives good choices for new pipeline jobs.
Note: Companies using RTP have fewer leaks, less fixing, and less pollution. This helps both the business and the planet.
Unitedpipe keeps making RTP better, helping customers work faster and safer. Its pipes do well in far away, tough, or rule-heavy places. Workers who want strong, cheap, and green pipelines should look at Unitedpipe for help.
Reinforced thermoplastic pipe is used a lot in oil and gas pipelines. Companies pick it for jobs like moving water, getting rid of waste, and gathering oil and gas on land. It is also used for home gas lines and fixing wells. Out at sea, it helps with putting chemicals in, shutting down old pipes, and other work. In deep water, thermoplastic composite pipe is used for flowlines, risers, and jumpers. These pipes can handle very high pressure, up to 10,000 psi, and work deep underwater, down to 3,000 meters.
Application Location | Pipe Type | Common Applications | Operating Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Onshore | RTP | Water injection, transport, disposal, gathering lines | Up to 65°C, 5 ksi (3.1–10.3 MPa) | Handles hydrocarbon, water, gas; limited pressure |
Offshore (Shallow Water) | RTP | Chemical injection, intervention | Max 42 bar, limited bore diameter | Requires extra procedures for gas service |
Offshore (Deepwater) | TCP | Subsea flowlines, risers, jumpers | Up to 689 bar, 3,000 mwd, 240°C | Certified for sweet/sour crude, gas, whole well stream |
Big oil and gas companies like Cenit, TGI, and Ocensa use RTP in hard places. One example is a 68 km pipeline in Lake Maracaibo. This shows RTP is flexible and does not rust.
Studies show reinforced thermoplastic pipe works well in the field. It does not rust and can handle hot and cold. This makes it good for underwater and tough places. Companies use it for flowlines, risers, and umbilicals, especially in deep water. Thermoplastic pipes can last from 10 to 100 years. This means they work for a long time.
Thermoplastic pipes cost less than steel pipes.
They need less fixing and are safer to use.
Real projects show they work well on land and at sea.
North America uses RTP the most because of shale oil. Europe and Asia-Pacific are using more RTP too. Rules like API 15HR and ASTM help keep pipes safe and strong. The market is growing fast because of new energy rules and cleaner energy needs. Companies trust RTP because it works well and saves money.
Industry experts like reinforced thermoplastic pipe for oil and gas pipelines because it has a special structure and many good features.
It does not rust, so it lasts a long time and can handle high pressure and heat.
It is light, so workers can put it in faster and save money over time.
It stops leaks and cracks, so work stays safe and runs well.
Feature | Benefit | Challenge Addressed |
|---|---|---|
Multi-layered pipe | Strong, bendy, and safe | Tough places, less downtime |
Lightweight design | Easy and quick to install | Hard-to-reach areas |
Chemical resistance | Fewer leaks, longer use | Rust, fixing problems |
Unitedpipe makes new RTP that works well. Companies who want safe and low-cost pipelines should look at Unitedpipe for their next jobs.
Reinforced thermoplastic pipe has layers of plastic and strong fibers. It does not rust and can handle high pressure. Oil and gas companies use it for pipelines that last a long time and are safe.
Feature | RTP | Steel Pipe |
|---|---|---|
Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
Corrosion | Does not rust | Rusts easily |
Installation | Fast, easy | Slow, complex |
RTP is quicker to set up and needs less fixing.
Companies use RTP for moving water, oil, gas, and chemicals. It works on land and at sea. It is good for new jobs and fixing old pipes.
RTP can last 10 to 40 years in use. It stands up to chemicals and weather. Taking care of it helps it last even more years.
RTP is better for nature because it leaks less and uses less energy to put in. It makes less pollution than steel pipes. Many companies pick RTP to help the planet.